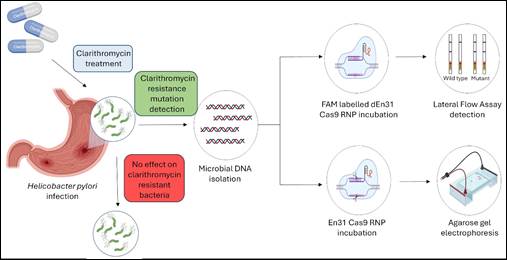
A new method developed by Indian researchers offers a significant advancement in diagnosing H. pylori, a common bacterial infection. This novel approach, utilizing a CRISPR-Cas9-based technique called FELUDA, can rapidly and accurately detect H. pylori and identify specific mutations that cause antibiotic resistance.
H. pylori infection affects millions worldwide, leading to various gastrointestinal issues including ulcers and even stomach cancer. Antibiotic resistance in H. pylori strains is a growing concern, making treatment challenging and increasing the risk of complications.
The researchers successfully employed an engineered Cas9 protein (en31-FnCas9) to detect H. pylori and its 23S rRNA gene mutations in patient samples. This method overcomes limitations of previous CRISPR-based approaches and provides a rapid, visual readout of infection status and resistance patterns.
This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize H. pylori diagnosis, particularly in resource-limited settings. By enabling accurate and timely detection of antibiotic resistance, this technology can guide personalized treatment plans, improve patient outcomes, and address the global public health challenge of H. pylori infection.