Introduction
Paper has been an integral part of human civilization, shaping how we communicate, record, and share knowledge. From its humble beginnings in ancient China to the modern advancements in sustainable production, paper’s evolution is a testament to human ingenuity. This blog delves into the history of paper, current technologies, types, classifications, and environmental innovations, and deciphers the meaning of GSM in paper.
The Historical Evolution of Paper
The origins of paper date back to 105 AD in ancient China, where Cai Lun, a court official, developed the first known papermaking process. He used a mixture of mulberry bark, hemp, rags, and water to create sheets that could be dried and used for writing. Prior to this, materials like papyrus in Egypt and parchment made from animal skins served as mediums for writing.
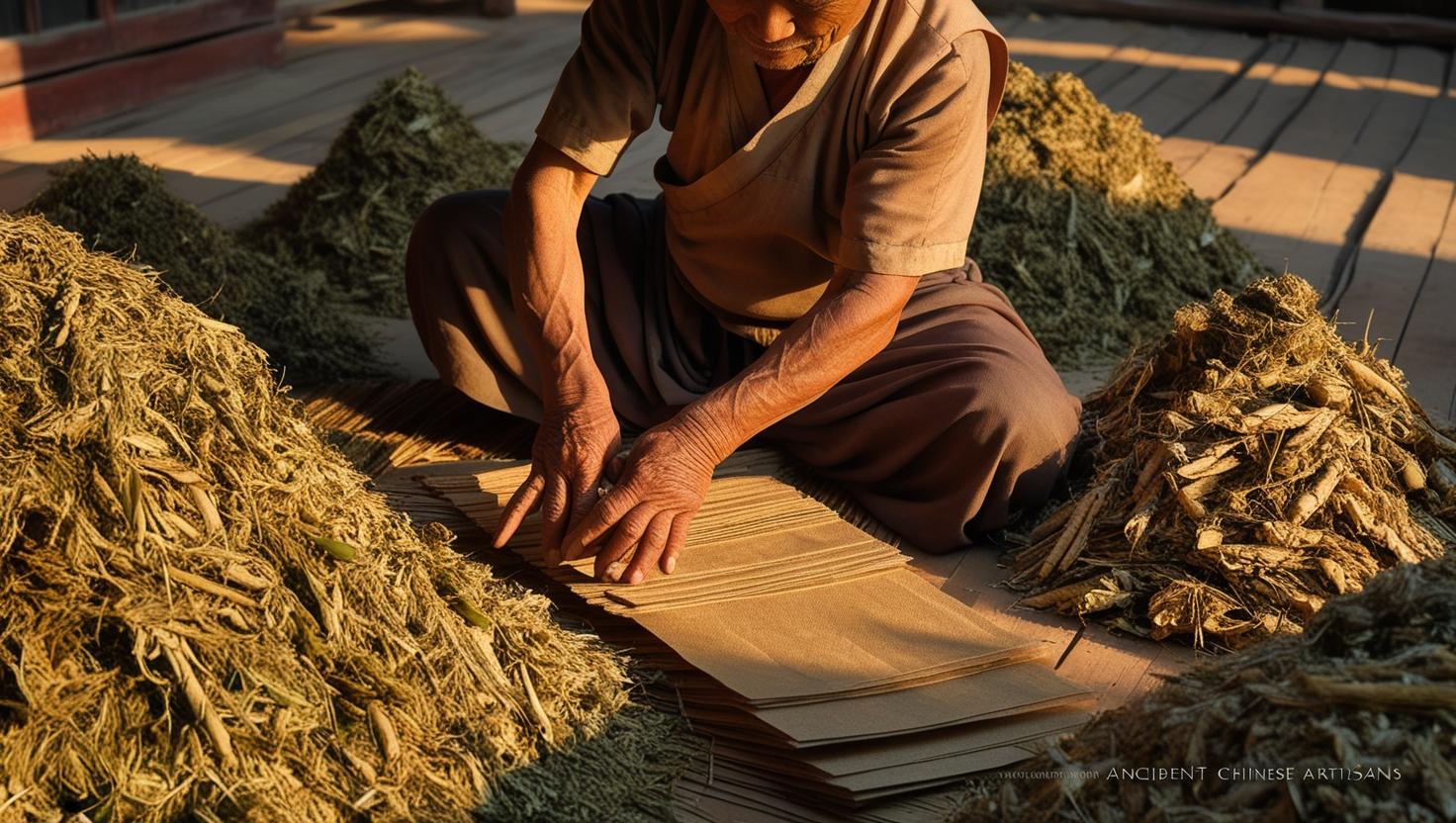

As trade routes expanded, papermaking spread to the Islamic world by the 8th century and later to Europe in the 12th century. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century accelerated paper’s demand and production. The Industrial Revolution brought mechanized papermaking processes, making paper affordable and accessible worldwide.
Modern Papermaking Technologies
Today, papermaking involves a sophisticated blend of technology and engineering. Key advancements include:
- Pulping Process: Wood fibers or recycled materials are broken down into pulp using mechanical, chemical, or hybrid methods.
- Mechanical Pulping: Produces lower-quality paper but is economical.
- Chemical Pulping: Delivers stronger and higher-quality paper by removing lignin.
- Bleaching: Modern techniques use eco-friendly, chlorine-free methods to whiten paper.
- Machine Production: High-speed machines like Fourdrinier and cylinder machines streamline production, ensuring uniform quality.
- Recycling Technologies: Advanced methods reclaim fibers from used paper, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Types of Paper Produced Today

Paper types vary based on their use and composition. Some common categories include:
- Printing and Writing Paper: Used for books, magazines, and office supplies.
- Tissue Paper: Includes toilet paper, facial tissues, and napkins.
- Packaging Paper: Covers kraft paper, corrugated cardboard, and coated paper for boxes.
- Specialty Paper: Includes photographic paper, security paper, and filter paper.
Classification of Paper by Making and Quality
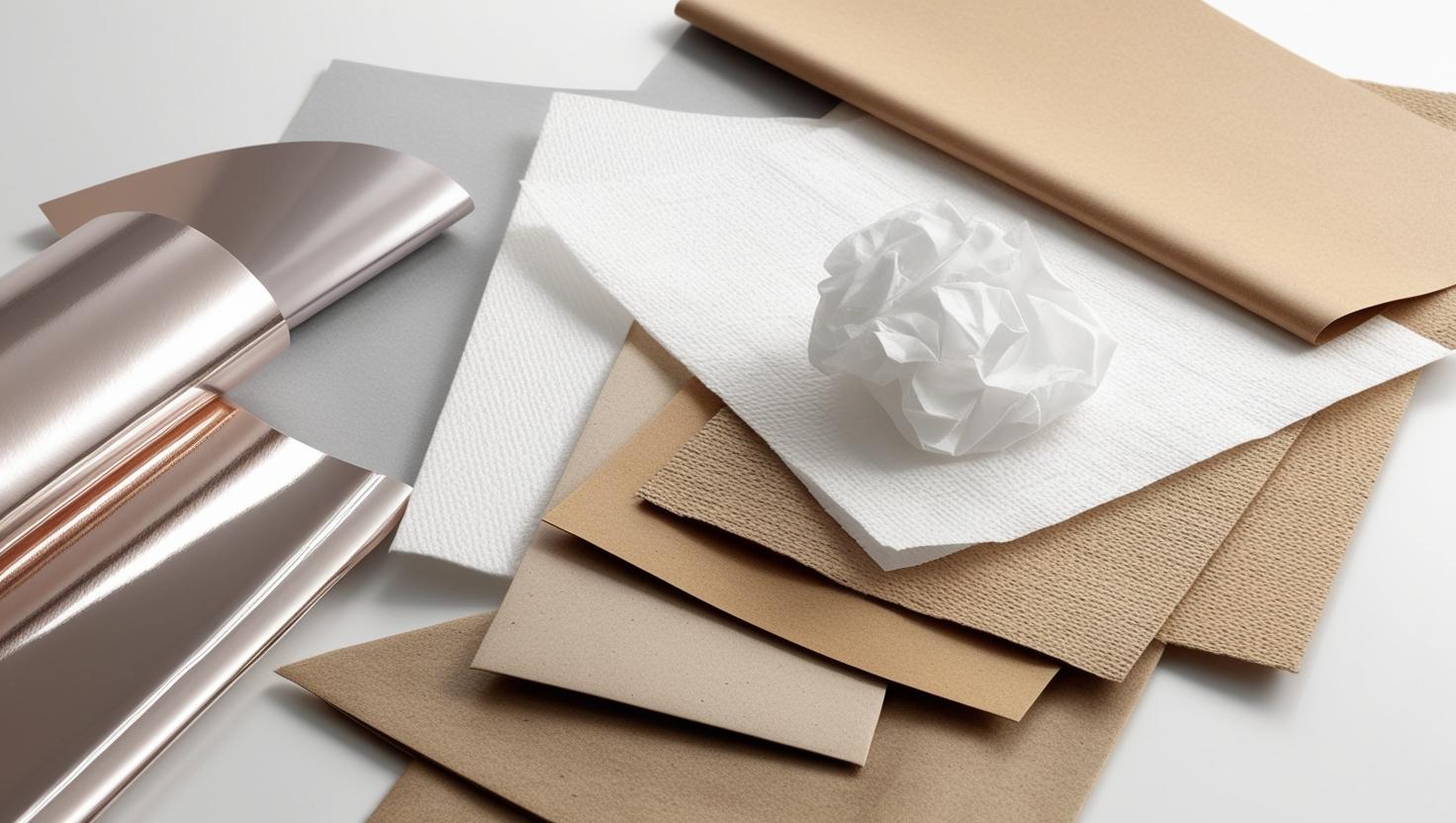

Paper can be classified based on its manufacturing process and quality:
- Handmade Paper: Crafted manually, often used for artistic and decorative purposes.
- Machine-Made Paper: Produced using industrial machines, available in various grades.
- Uncoated Paper: Raw finish, ideal for printing and writing.
- Coated Paper: Features a glossy or matte layer for enhanced print quality.
- Recycled Paper: Made from post-consumer waste, emphasizing sustainability.
Sustainable Innovations in Papermaking



The paper industry has made significant strides in minimizing its environmental footprint. Key initiatives include:
- Eco-Friendly Raw Materials: Using bamboo, hemp, and agricultural residues as alternatives to wood.
- Water Conservation: Recycling water within the manufacturing process.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Carbon Neutrality: Reducing emissions through sustainable practices and carbon offsets.
- Recycling Programs: Encouraging the collection and reuse of paper waste.
Understanding GSM in Paper
GSM (grams per square meter) measures the weight of paper. It indicates the paper’s thickness and density. For example:
- 70-90 GSM: Common for office use and printing.
- 120-200 GSM: Ideal for brochures and posters.
- Above 250 GSM: Used for business cards and premium packaging.
Conclusion
From ancient papyrus scrolls to modern recyclable sheets, the journey of paper underscores humanity’s relentless quest for innovation. As sustainability takes center stage, the paper industry continues to adapt, ensuring that this timeless medium remains relevant while respecting our planet. Understanding the science, types, and advancements of paper helps us appreciate its indispensable role in our daily lives.




