Researchers have developed a novel nano-formulation to enable the sustained release of 17β-Estradiol, a hormone critical in managing Parkinson’s Disease (PD). This breakthrough could pave the way for safer and more effective treatments for PD patients.
Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases often result from an imbalance of 17β-Estradiol (E2) in the brain. However, peripheral side effects and limited understanding of E2’s molecular mechanisms have hindered its therapeutic potential.
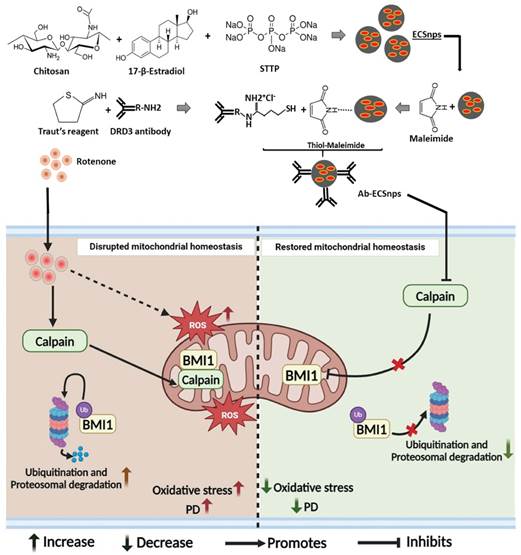
A team from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, has engineered a solution: Dopamine Receptor D3 (DRD3)-conjugated chitosan nanoparticles loaded with 17β-Estradiol. This innovative delivery system ensures sustained release of E2 directly to the brain.
The formulation showed promising results by inhibiting the mitochondrial translocation of calpain, a process linked to neuronal damage. This approach protected neurons from rotenone-induced mitochondrial damage while alleviating behavioral impairments in rodent models.
Additionally, the study made a novel discovery that BMI1, a protein in the PRC1 complex regulating mitochondrial homeostasis, is a substrate of calpain. The targeted nano-formulation successfully restored BMI1 expression by preventing its degradation through calpain inhibition.
Published in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers, the research sheds light on E2’s role in regulating oxidative stress in Parkinson’s patients. With further studies to explore long-term safety and improved delivery mechanisms, this breakthrough holds promise for a safer and more targeted drug to enhance the quality of life for individuals with PD.